|
Mental Disorders: Overheads
Mental Disorders
-
Basic concepts
-
What is a mental disorder?
-
Perspectives on mental disorders
-
Anxiety Disorders
-
Schizophrenia
-
Eating Disorders
What is a mental
disorder?
-
Mental disorder = maladaptive
psychological process
-
Maladaptive psychological process
must:
-
Involve clinically significant
distress and/or impaired functioning
-
Have an internal source
-
Be manifested involuntarily
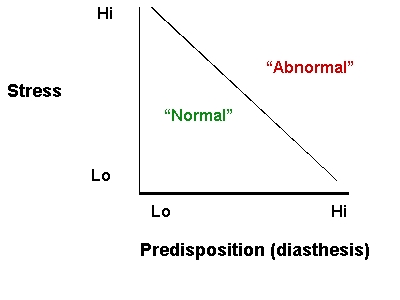
Diasthesis-stress
model
The fine
line between “normal” and “abnormal”
Prevalence
Perspectives
-
Biological/Medical Model
-
genetic disorder
-
neurochemical dysfunction
-
disease
-
Cognitive, Behavioral, Psychodynamic
Perspectives
-
Interaction with the environment
-
[Conflicts among id, ego, superego]
-
Sociocultural Perspective
-
Interaction with the larger environment
-- culture
Eating
Disorders
-
Anorexia Nervosa
-
Bulimia Nervosa
-
Compulsive Overeating
Diagnostic Criteria
-
Refusal to maintain body weight
(< 85% normal weight or BMI < 17.5)
-
Intense fear of gaining weight
-
Undue influence of body image
on self evaluation
-
Amenorrhoea (in postmenarcheal
women)
Checklists:
 Internet Mental Health
Internet Mental Health
 University of Minnesota - Deluth Check list
University of Minnesota - Deluth Check list
 Anorexia Nervosa and Related Eating Disorders, Inc.
Anorexia Nervosa and Related Eating Disorders, Inc.
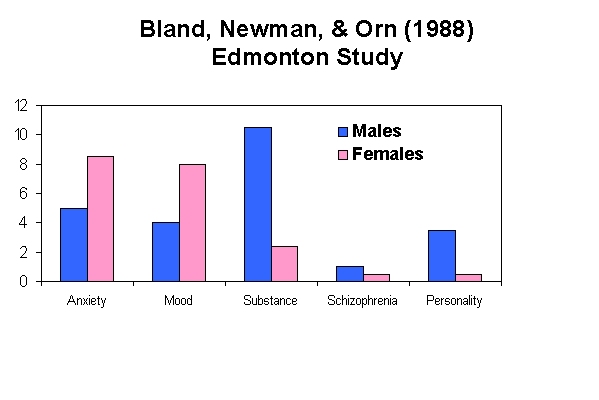
Prevalence
-
Third most common chronic illness
in adolescent females
-
Estimated to affect up to 5% in
adolescent females
-
Rate increasing in males and females
Meeting
the criteria for a mental disorder
-
Clinically significant distress
and/or impaired functioning
-
Life-threatening medical disorder
-
Social isolation
-
Internal source
-
No medical explanation for weight
loss
-
Be manifested involuntarily
-
Even during treatment, anorectics
cannot eat
Biological/Medical
Perspective
-
Genetic link
-
Anorexia in 9 of 16 monozygotic
twins but 1 of 14 in dizygotic twins
-
20% of anorectics have family
member with eating disorder, compared with 6% for other mental disorders
-
Neurochemical disorder
-
Abnormally high levels of endogenous
opioids in CSF
-
Disease link
-
Sudden onset OCD and/or anorexia
following strep infection
Psychodynamic
Perspective
-
Inability to accept developing
sexuality and independence
-
Fear of becoming like her mother
-
Reaction to controlling parents
Behavioural
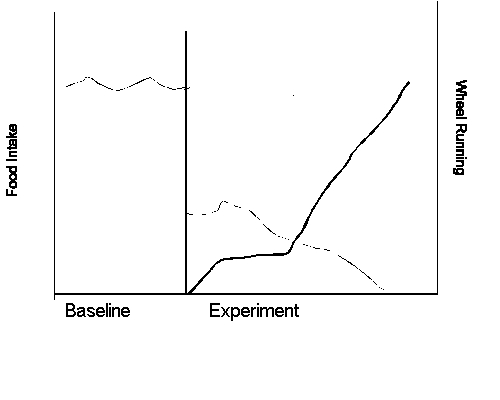
Perspective: Activity Anorexia
-
Anorexia is induced and maintained
by abnormal levels of exercise
-
Intense physical activity central,
not symptomatic
-
Adaptation gone awry:
-
Limited food source
-
Travel great distance at great
speed to find more food
-
Something goes wrong: Exercise,
not obtaining food, becomes reinforcing
Epling,
Pierce, & Stefan (1983)
Sociocultural
Perspective
-
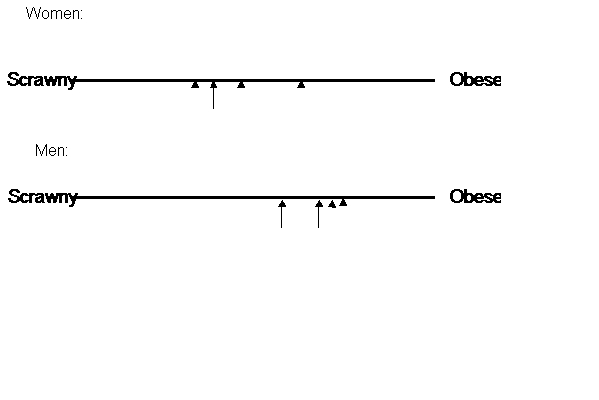
Thin society
-
1950s: 7% men, 14% women reported
dieting
-
1990s: 24% men, 40% women report
dieting
-
Eating disorders equal in all
social classes
-
Eating disorders equal among Whites
and African Americans
|