Path Integration and Cognitive Mapping
Path Integration
Compute present location from past trajectory
Return to starting point via direct route
Integrate velocity with respect to time
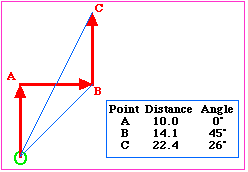
Errors accumulate
Catglyphis Homing
Muller and Wehner (1988)
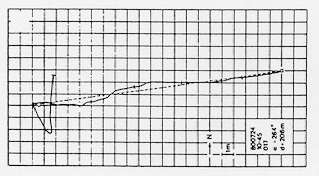
Example of a typical return path of a Cataglyphis forager. Homing path of a single ant (dark line). Fixes (cross bars) taken every ten seconds. The hatched line shows the direct path between the foraging site (open square) and the nest (open circle). (From Wehner & Srinivasan, 1991, p. 318.)
- Plastic channels
- Two-leg trajectory to food source
- Systematic errors depending on angle of channel
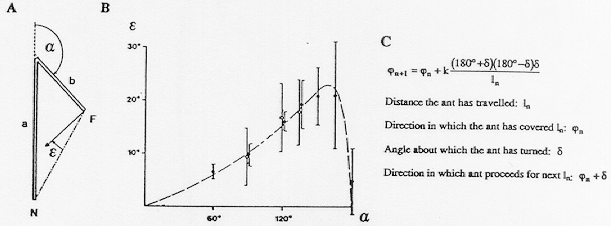
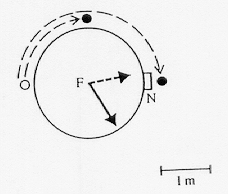
Design of Muller and Wehner's (1988) two-legged experiment. (A) Experimental set-up. N = nest; F = food source; a and b = length of first and second segment of the training route, respectively; alpha = turning angle; epsilon = error angle as recorded from homing ants captured at F and released in the open test area. (B) Results. Error angles (y-axis) plotted for different turning angles (x-axis), where a = 10m and b = 5m. The ants were allowed to use either their sun compass (open circles) or their polarization compass (filled circles). Confidnece limits given for P = 0.99. The data depict 1412 experiments performed on 310 ants. The dashed line depicts the error angles as calculated by the computational model. (C) The computational model used to fit the curve in (B) with description of terms. (Adapted from Muller and Wehner, 1988, p. 5288.)
- Errors with sharp backwards turn
- Naturally rare
- Equal number left and right turns
- Mathematical short-cuts
Nest Finding by Cataglyphis
Wehner and Srinivasan (1981)
- Wide looping turns
- Re-centre searching behaviour
- 10,000 square meter search area
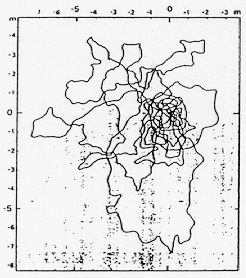
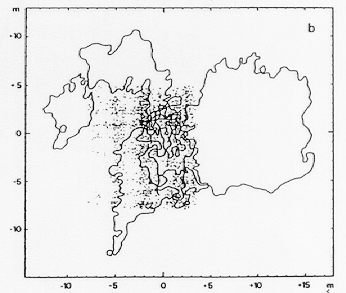
Paths of single Cataglyphis foragers searching for their nest opening. The ants have been displaced to a test area so that they can not, in fact, ever locate the actual nest entrance. The ficticious location of the nest opening is at the coordinates (0,0) on each figure. Notice that the ants begin by searching near the belived location of the nest entrance then expand their search outwards in a series of wide looping turns that eventually return to the believed point of the nest opening.
- Not searching for nest opening but for salient landmarks
Golden Hamster Displacements
Etienne, Maurer, and Saucy (1988)
(From: Etienne, Maurer, and Seguinot, 1996, p. 203.)
(From: Etienne, Maurer, and Seguinot, 1996, p. 203.)
(From: Etienne, Maurer, and Seguinot, 1996, p. 203.)
Landmarks and Path Integration
Corrects for errors
Hierarchy
Burkhalter (1972)
- Landmarks overrode distance estimator
Etienne et al. (1996)
- Degree of discrepancy matterns
- 90 degree: use path integration
- 180 degree: use landmark
(From: Etienne, Maurer, and Seguinot, 1996, p. 207.)
Cognitive Maps
Tolman (1948)
- Cognitive map: routes, paths, environmental relationships in the CNS
- Strip-like maps
- Comprehensive maps
- Topographic maps
- Maze learning
- Short-cuts
- Lashley (1929): rat out of maze...reaches goal
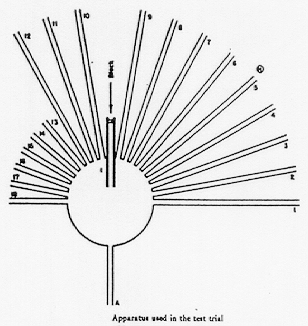
- Tolman, Ritchie, and Kalish (1946)
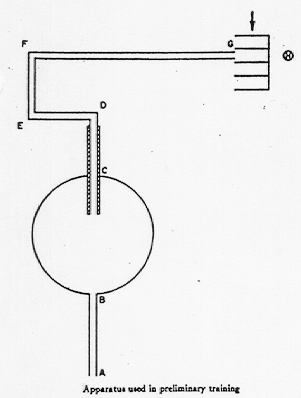
(From: Tolman, Ritchie, and Kalish, 1946, p. 16 and 17)
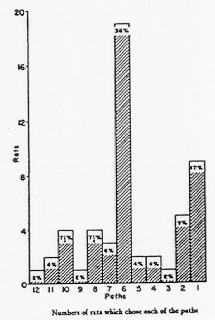
(From: Tolman, Ritchie, and Kalish, 1946, p. 19)
O'Keefe and Nadel (1978)
- Routes (landmarks close to goal)
- Maps (short-cuts)
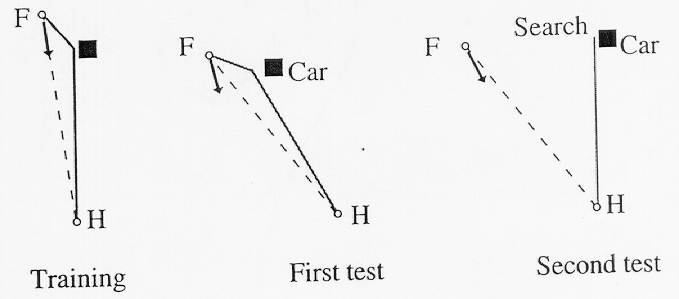
(From: Menzel, Geiger, Chittka, Joerges, Junze, and Muller, 1996, p. 142)
Gallistel (1990)
- Cognitive map
- A CNS record of macroscopic geometric relations among environmental features used to plan movements
- Computational-representational framework
- Isomorphisms: formal correspondences between distinct systems of mathematical study
- Maps: metric, affine, projective, topology
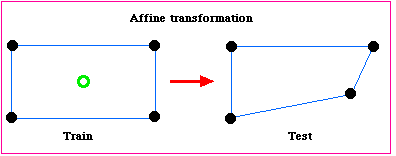
- Metric geometry: distance and angle
- Cogntive maps are metric maps
Cogntive Maps in Honey Bees?
Gould (1986)
- Tested if bees could find novel route
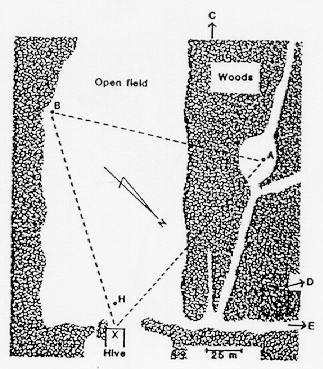
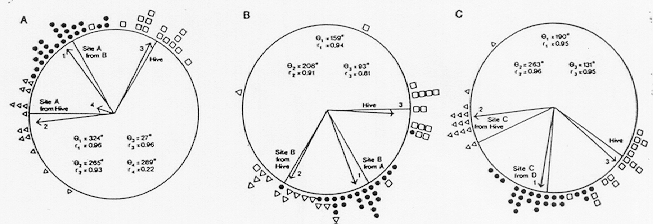
- Concluded bees have cognitive maps
Wehner, Bleuler, Nievergelt, and Shah (1991)
- Tried to replicate Gould (1986)
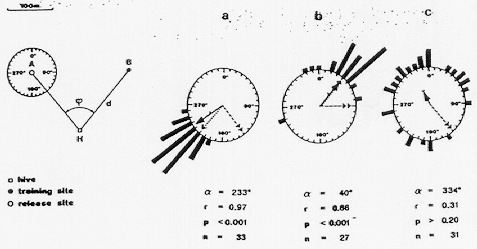
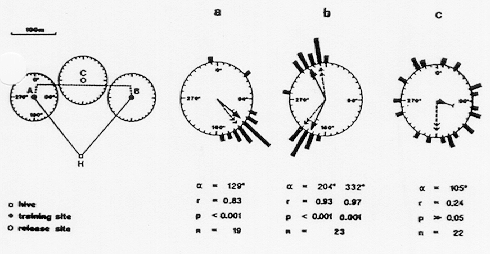
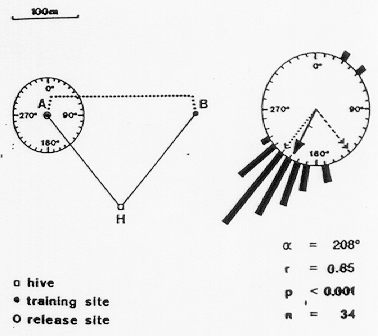
- Concluded bees use path integration and landmarks (catch features)
Blind Cave Fish
Teyke (1989)
- Swim patterns in familiar and unfamiliar environment
- Lateral line organ
- Tank exploration
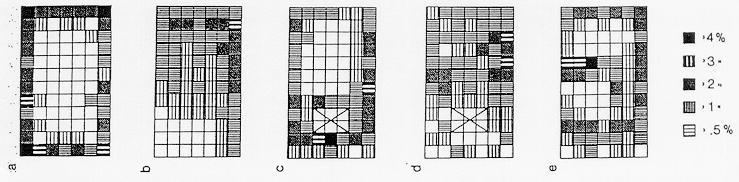
- Tank shape
- Claims cognitive map
Return to 403 course page.





















