|
Mental Disorders: Overheads
Mental Disorders
-
What are mental disorders?
-
Perspectives on mental disorders
-
Phobia!
What is a mental
disorder?
Mental disorder = maladaptive psychological process
Maladaptive psychological process must:
-
Involve clinically significant distress
and/or impaired functioning
-
Have an internal source
-
Be manifested involuntarily
Perspectives
on Cause
Psychodynamic Perspective
-
Conflicts among id, ego, superego
Biological/Medical Model
-
Genetic disorder, neurochemical dysfunction,
disease
Cognitive/Behavioral Perspective
-
Interaction with the environment
Sociocultural Perspective
-
Interaction with the larger environment
culture
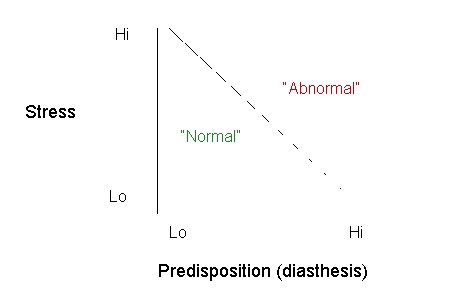
Diasthesis-Stress Model
-
The fine line between "normal" and "abnormal"
Phobia!
"The only thing we have to fear is
fear itself - nameless, unreasoning, unjustified terror which paralyzes
needed efforts to convert retreat into advance." -- FDR, 1933.
"My heart starts beating so fast that
it feels like itís going to explode. My throat closes and I canít breathe
so I start to choke. My hands start sweating and I get so dizzy I have
to hold onto the furniture or the wall to keep from falling or fainting.
I know Iím going to die. I want to run but I donít know where." --Phobia
sufferer.
Types of phobias
Agoraphobia (with or without panic attacks)
-
Irrational anxiety about being in places
from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing
Social Phobia
-
Irrational anxiety elicited by exposure
to certain types of social or performance situations, also leading to avoidance
behavior.
Simple Phobia
-
Persistent and irrational fear in the
presence of some specific stimulus which commonly elicits avoidance.
-
Animal, natural environment, blood-injection-injury,
situational, or other types
Symptoms
Persistent and irrational panic, dread, horror, terror
in a harmless situation.
Person realizes that the fear goes beyond normal
boundaries.
Reaction is automatic, uncontrollable, persuasive,
and practically takes over thought.
Person suffers from all the physical reactions associated
with extreme fear, i.e.., rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, trembling,
overwhelming desire to flee.
Avoidance or flight interferes with every-day activities.
Meeting the criteria
for a mental disorder
Clinically significant distress and/or impaired functioning
-
Agoraphobics donít leave home.
-
Acrophobics will not live in high-rises.
Internal source
-
Auroraphobics may have never seen the
Northern lights.
Be manifested involuntarily
-
Arachnophobics cannot pick up a plastic
spider.
-
All phobics recognize their irrational
fear but can do nothing about it.
Phobia Scale
Rate pictures
-
How fearful does this make you
feel?
1=least fearful
3=somewhat fearful
5=very fearful
-
To what extent would you try
to avoid encountering this situation?
1=wouldnít avoid
3=might avoid
5=avoid at all costs
| Picture |
Description |
Fear Rating |
Avoidance Rating |
| 1 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
|
|
|
Perspectives
on Phobia...
Psychodynamic Perspective
-
Fear of abandonment by a cold or nonnurturing
mother.
-
Generalized to phobic or other anxiety
disorder.
Biological/Medical Model
-
Greater blood flow and metabolism in
right hemisphere than in left.
-
Humans have a predisposition to develop
certain phobias and not others.
-
Identical twins reared apart have developed
identical phobias.
Cognitive/Behavioral Perspective
-
Previous experience or model.
-
Adaptive advantage to learn very quickly.
-
Social phobics tend to have been shy,
timid children
Sociocultural Perspective
-
Cultural predisposition, e.g., taijin
kyofusho.
-
Evolutionary basis in patterns of dominance
and submission.
|