Membrane Potential
Voltage difference across plasma membrane
Resting potential
- -40 mV to -90 mV
- Negative relative to extracellular

Depolarized
- Less negative than resting potential
Hyperpolarized
- More negative than resting potential
Action Potential
Message that goes down the axon
A large depolarization of the axon
Threshold
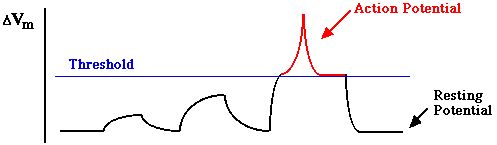
All or none
- Either threshold is reached or nothing happens
- Can not stop an action potential
Refractory period
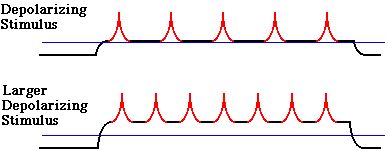
Frequency coding
- Larger depolarizing stimulus, greater firing rate
 �
�
Molecular Basis for Action Potentials
Cell membrane
- Porous skin of the neuron
- Intracellular fluid
- Extracellular fluid
- Ion channels
- Balance of charge
- Intracellular more negative than extracellular
- Resting potential (negative)

Action potential
- Initiation phase
- Depolarization phase
- Sodium ions enter
- Concentration gradient
- Electrical gradient
- Repolarization phase
- Sodium channels close
- Potassium channels open
- Sodium-potassium pump
�
Central Pattern Generators
Rhythmic muscular contraction
- e.g., walking, swimming, peristaltic movement
Opposing muscle groups working in coordination
- Contract, relax, contract, relax, etc.
Required network of neurons
- Different neurons innervate different muscles
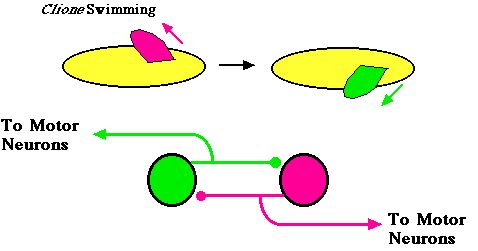
Simplest CPG
- Two neurons
- Reciprocal inhibition
- Postinhibitory rebound
- Cell becomes more excitable after hyperpolarization (threshold is reduced)
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
Computer programs
Must be trained
- Learning
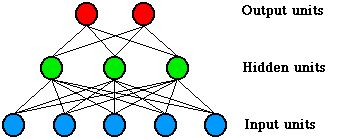
Based on neuronal structure
- Input units
- Hidden units
- Output units
Are ANNs just like real nervous systems?
What use are ANNs?
- Simulation
- Metaphor
- Hypothesis testing
Nervous System Organization
Central nervous system (CNS)
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Non-regenerative
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- Nerves outside the CNS
- Regenerative
Classes of neurons
- Sensory neurons
- Carry information from sensory organs to CNS
- Interneurons
- Only in the CNS
- Carry information from one neuron to another
- Organize and integrate information
- Motor neurons
- Carry information to muscles and glands
PNS Systems
Skeletal
- Muscles attached to bones
- Externally observable movements
- Neurons extend directly from CNS to muscle
Autonomic
- Visceral muscles and glands
- Indirect neuronal action from CNS to ganglion to target site
- Sympathetic division
- Immediate responses to stressful stimuli
- Parasympathetic division
- Regenerative, energy-conserving processes
Return to Psych 104 Lecture Index page.






