Nervous System
Neuronal level
- Gray text pages 163-166, 185-190
Action potentials and nervous system organization
- Gray text pages 183-185, 166-179
Brain organization
- Gray text pages 179-182, 191-199
Levels of Neural Organization

To understand the brain understand all levels
Neurons
Functions
- Signaling
- Information transfer
- Within cells
- Between cells
Types of Neurons
- Neuroglia
- Astrocytes
- Myelin
- Oligodendrocytes
- Schwann cells
- Neurons
- Sensory
- Interneuron
- Motor
Structure
- Soma
- Axon
- Terminal
- Dendrites
Soma

Like any other cell
- Nucleus, mitochondria, plasma membrane

Axon
"Telephone wires" of the nervous system
Myelin sheathe
- Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
- Schwann cells (PNS)
Axonal transport
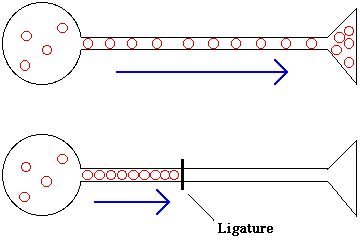
- Microtubules ("axon escalators")
- Neurotransmitters
- Proteins
Axon Terminal
The "transmitter"
Connects with
- Dendrites (common)
- Soma (common)
- Other axons (rare)
Communicates via
- Chemical transmitters
- Electrical signals
- Excitatory or inhibitory signals
Dendrites
The "receivers"
Connects to axon terminals
Transfers signal received from another neuron to the soma
Axons and dendrites form synapses!
The Synapse
Where neurons communicate with one another
- Presynaptic cell
- Postsynaptic cell
- Chemical and electrical synapses
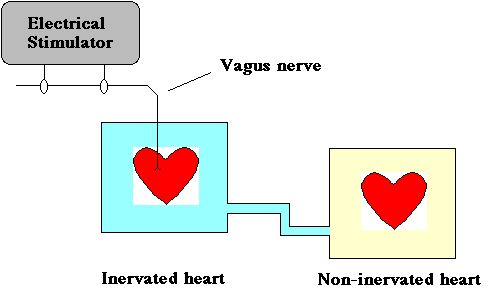
Two hearts, no brain...
- Demonstrates chemical (neurotransmitter) synapse
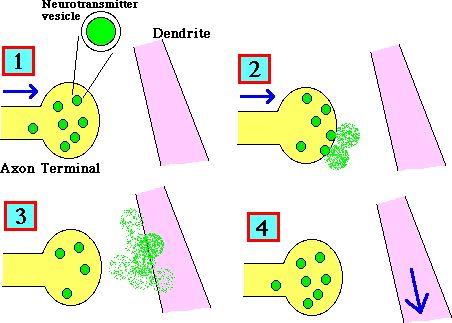
Chemical Synapses
Asymmetric morphology
- Presynaptic
- Axon terminal (contains neurotransmitter)
- Postsynaptic
Synaptic cleft
- Space between pre- and postsynaptic elements
Transmission of signal
- Axon terminal releases neurotransmitter
- Neurotransmitters diffuse across synaptic cleft
- Postsynaptic receptors uptake neurotransmitter
- Signal travels to next neuron (unidirectional!)
Electrical Synapses
Symmetrical morphology
Pre- and postsynaptic elements physically indistinguishable
Bi-directional!
Gap junctions
Ion movement through gap junction
- Mediates signaling
- Low resistance pathways
Very fast
- Neurons are physically coupled
- No synaptic cleft to diffuse across
Dye coupling: Are their gap junctions here?
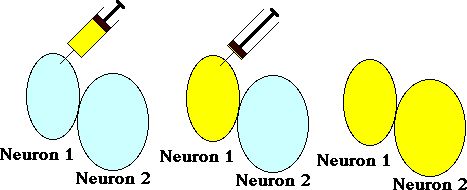
Brain Drain...
Computers are often compared to human brains. In what ways are computers similar to brains? How are computers different from brains?
What neuronal tasks would benefit more from electrical synapses than chemical synapses?
What would go wrong if action potentials could travel both up and down axons?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) can regenerate from damage whereas the central nervous system (CNS) can not. Could this possibly have some evolutionary advantage?
Return to Psych 104 Lecture Index page.









