From Last Class...
Single Gene Disorders
Punnett Squares
Chromosome Disorders
- Sex chromosomes
- Down syndrome
Polygenetic Effects
Heritability
Intelligence
Francis Galton (1822-1911)
- Intelligence
- Twin studies
- Genetic basis
John Stuart Mill (1806-1874)
- Human rights
- Environmental basis
Correlation Coefficients
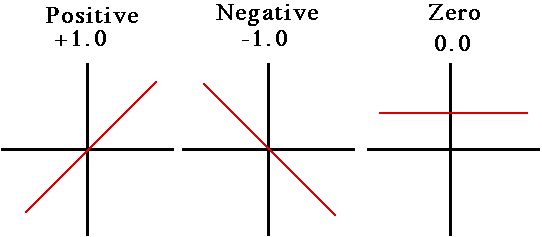
IQ Correlation in Twins
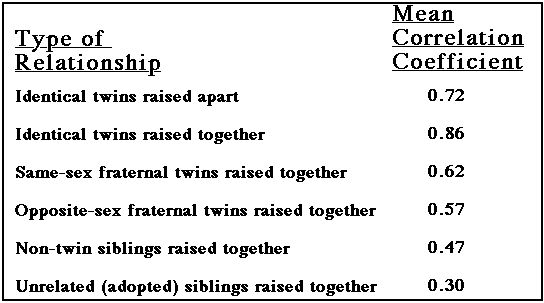
For siblings raised together:
- Closer the genetic relation, the higher the IQ correlation
For identical twins raised apart:
- IQ correlation higher than fraternal twins raised together
Genetic component in IQ
The Environmental Influence
Non-related children raised in the same home
- No genetic similarity
- Some degree of environmental similarity
Young children
- Average correlation coefficient of +0.30
Older children
- By age 18, -0.03
- Even genetically related children show reduced correlation coefficients as children get older
- Greater genetic relationship --> less decline
Conclusions:
- High parental influence on IQ when children young
�
IQ and Race
Genes or environment?
French study
- Lower class children adopted into middle/upper class homes
- Adopted children had IQ of 109
- 14 points higher than non-adopted lower class children
- No different than children born to middle/upper class homes
American study
- Black children adopted into white middle/upper class homes
- Adopted children showed significantly higher IQ than non-adopted blacks
- No different from white children from middle/upper class homes
Conclusion:
- "Racial" differences in IQ due to environmental differences
�
Schizophrenia
Affects both sexes equally
1% of the population worldwide
- Constant across cultures
- Another 2-3% have schizotypal personality disorder
Diagnosis
- Psychotic phase
- Bizarre delusions
- Prominent hallucinations (usually auditory)
- Disordered thoughts and incoherence
- Residual phase
- Eccentric behaviour
- Socially isolated
- Poverty of speech
- Poor attention span
Genes and Schizophrenia
Franz Kallmann (1938)
- 1% rate worldwide
- 15% rate in certain families
Twin studies
- Monozygotic twins
- Essentially identical genotype
- Fraternal twins
- Share half their genotype
- If strictly genetic:
- Monozygotic twins should have same tendency to develop schizophrenia
- Concordance
Monozygotic twins
Fraternal twins and non-twin siblings
General population
Conclusions:
- High genetic component
- Not strictly genetic
Environment and Schizophrenia
Could high monozygotic twin concordance be due to:
- Psychological trauma of having a twin with schizophrenia?
- Higher rates of perinatal trauma?
More adoptee studies
- Compare:
- Schizophrenia in adopted children of schizophrenic biological parents
- Adopted children of normal parents
- Schizophrenia higher among children whose biological parents had schizophrenia
Conclusion:
- Child rearing plays minor role in development oF schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is not a single gene disorder
Schizophrenia is a polygenetic effect
- Genes and environment interact
- Chromosome 6
Pre-natal flu
- May contribute to some cases of late onset schizophrenia
�
Chapter 3 in Capsule
Nature and Nurture
DNA, Chromosomes, Genes, Proteins
Genotype, Phenotype, Dominant, Recessive
Genetic diversity
Mendelian genetics, Punnett squares
Single gene disorders
Chromosome disorders
Polygenetic effects on behaviour
Heritability
Intelligence and IQ
Schizophrenia
�
Thoughts for the Bus Ride Home
Why are adoption studies so important in psychology?
What does a correlation coefficient tell you?
Luke Skywalker is a powerful Jedi Knight. He is strong in the ways of the Force. Yoda and Obi wan said the Force was strong in Luke's family. Hence, we assume there is a genetic component to being able to use the Force. Let us assume that the Force gene is recessive (otherwise the galaxy would be full of lightsabre swinging Jedi Knights). If Luke's father (the infamous Darth Vader) had been homozygous recessive, and his mother had been heterozygous recessive, what percentage chance was there that Luke would be homozygous recessive for the Force gene? How about for his twin sister, Princess Leia?
Return to Psych 104 Lecture Index page.

